9 Remote Work Security Best Practices for 2025
The shift to remote work has redefined professional freedom, empowering digital nomads and independent professionals to build careers from anywhere on the globe. This newfound autonomy, however, introduces a complex set of security challenges. The traditional office perimeter has vanished, and connecting from a bustling café in Lisbon or a quiet coworking space in Bali means your digital assets are constantly exposed to new threats. Your laptop, phone, and personal network are now the front lines of your digital defense, making a proactive security posture an absolute necessity.
This guide goes beyond generic advice. We will provide a comprehensive roundup of the most critical remote work security best practices that form a resilient cybersecurity framework. We won’t just tell you what to do; we will show you how to implement these strategies with actionable steps and real-world examples specifically for the modern remote professional.
From adopting a Zero Trust mindset to implementing robust endpoint detection, you will learn to build a multi-layered defense system that protects your data, your clients’ information, and your professional reputation.
Inside this playbook, we’ll break down nine essential security pillars, including:
- Zero Trust Network Architecture: Why you should never trust and always verify.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): The non-negotiable layer for all your accounts.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Implementation: Securing your connection on any network.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Advanced threat hunting for your devices.
- Secure Cloud Storage and Data Loss Prevention: Protecting your data in transit and at rest.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Turning yourself into the strongest link in your security chain.
Mastering these concepts is the key to securing your freedom and ensuring your remote career is both successful and secure.
1. Zero Trust Network Architecture
Traditional security models operate on a “castle-and-moat” principle, trusting anyone inside the network perimeter. In the era of remote work, where the perimeter is dissolved, this approach is dangerously outdated. Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA) completely inverts this model, operating on a single, powerful phrase: “never trust, always verify.”
This security framework requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources on a private network, regardless of whether they are sitting inside or outside the network perimeter. It assumes that a breach is inevitable or has likely already occurred, so it eliminates the concept of a trusted internal network. Access is granted on a least-privileged, need-to-know basis, significantly reducing an attacker’s ability to move laterally through your network if they compromise a single user account.
Why Zero Trust is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
Adopting a Zero Trust model is a foundational step in securing a distributed workforce. It directly addresses the challenges of remote access by ensuring that location is irrelevant to the security posture. Every connection, every data request, and every user action is treated as a potential threat and must be authenticated and authorized. This continuous validation process is critical when employees connect from unsecured home Wi-Fi, public coffee shops, or co-working spaces.
Industry giants have pioneered this approach, proving its effectiveness at scale. Google’s BeyondCorp initiative is a prime example, securing corporate access without a traditional VPN. Similarly, Microsoft has built a comprehensive Zero Trust security model into its ecosystem, showcasing its adaptability for modern digital environments.
The following infographic summarizes the core principles and benefits of implementing a Zero Trust architecture.
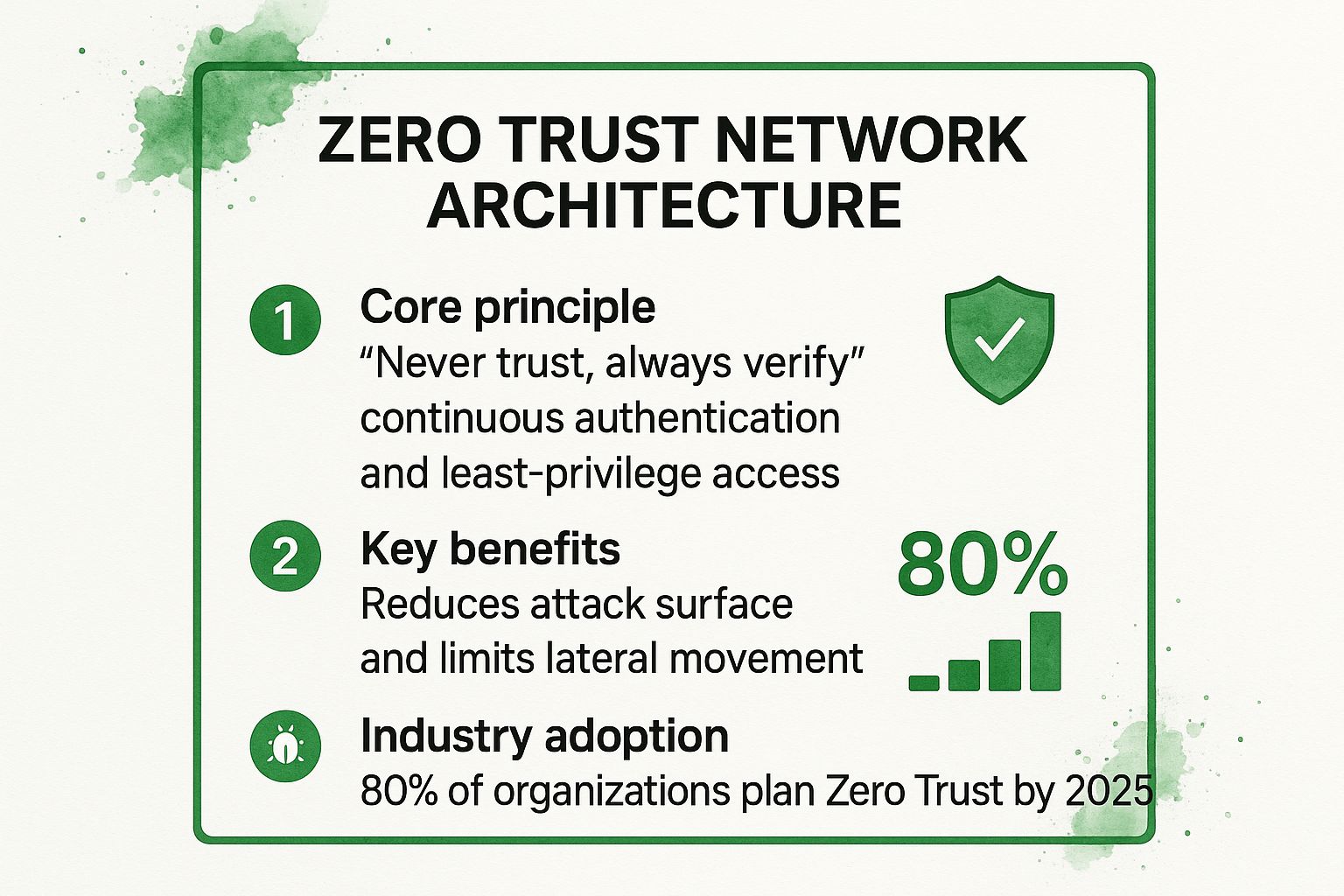

As the data shows, Zero Trust is not a niche concept but a rapidly growing industry standard for robust security. Its ability to shrink the attack surface makes it one of the most effective remote work security best practices available today.
How to Implement Zero Trust
Transitioning to a full Zero Trust model is a strategic journey, not a single product deployment. To make the process manageable, consider these actionable steps:
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot program for a specific high-risk application or a small, tech-savvy user group to work out kinks.
- Map Your Assets: Before you can protect your resources, you must know what they are. Map all network assets, data flows, and user access patterns to understand your current environment.
- Prioritize User Experience: A secure system that users bypass is not secure. Use tools like Single Sign-On (SSO) and contextual, risk-based authentication to reduce friction and improve the user experience.
- Invest in Training: Educate your team on why these new security measures are in place. When users understand the “why,” they are more likely to adopt the new processes without complaint.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
If passwords are the front door to your digital life, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is the deadbolt, the security chain, and the alarm system all in one. It’s a simple yet incredibly powerful security layer that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to an account or application. This approach moves beyond a single point of failure (a compromised password) by layering proof of identity through something you know (password), something you have (a phone or hardware token), and something you are (a fingerprint or face scan).
Even if a cybercriminal steals a user’s password, they are stopped in their tracks without the second verification factor. This makes MFA one of the single most effective controls you can implement to prevent unauthorized access to corporate resources. For remote workers accessing sensitive data from various locations and networks, enabling MFA is not just a recommendation; it is an absolute necessity.


Why MFA is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
Mandating MFA across all company applications, from email to cloud storage, drastically reduces the risk of account takeover attacks, which are a primary vector for data breaches. It provides a robust security baseline that protects company assets regardless of an employee’s location or the security of their local network. Given that a significant percentage of security breaches involve weak or stolen credentials, MFA directly mitigates this pervasive threat.
Pioneered by companies like RSA Security and now universally adopted by tech leaders such as Google, Microsoft, and Duo Security (now part of Cisco), MFA has become the gold standard for access control. Implementing Microsoft 365 MFA or Google Authenticator for G Suite accounts are common, effective first steps for any organization securing a remote workforce.
How to Implement MFA
Rolling out MFA effectively requires balancing security with user convenience. A poorly planned implementation can lead to frustration and resistance. Use these steps to ensure a smooth and secure deployment:
- Prioritize App-Based Authenticators: Encourage the use of authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator over SMS-based codes. SMS messages can be intercepted through SIM-swapping attacks, making apps a more secure option.
- Implement Adaptive MFA: Use risk-based or adaptive authentication policies. These systems can require MFA only when a risk factor is detected, such as a login from an unrecognized device or a new geographical location, reducing friction for everyday access.
- Provide Backup Options: Ensure users have multiple backup methods (e.g., recovery codes, a secondary device) to avoid getting locked out of their accounts. This is crucial for maintaining productivity.
- Train Your Team: Conduct training sessions to walk employees through the MFA setup process. Explain the “why” behind this security measure and provide clear instructions and support for troubleshooting common issues.
3. Virtual Private Network (VPN) Implementation
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a foundational technology for remote work, creating a secure, encrypted tunnel between a remote user’s device and the company network. It effectively extends the private network over a public one, like the internet, allowing employees to access internal resources as if they were physically present in the office. This process encrypts all data transmitted, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it.
This encrypted tunnel masks the user’s IP address and secures their connection, which is crucial when working from potentially insecure public Wi-Fi networks. By routing traffic through a secure server, a VPN ensures that sensitive company data remains confidential and protected from eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks. It is a vital layer of defense in any remote work security strategy.


Why VPN Implementation is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
Implementing a robust VPN is one of the most direct and effective ways to secure data in transit for a distributed workforce. It provides a straightforward solution to the inherent risks of using public internet connections. For digital nomads and remote professionals who frequently connect from cafes, airports, and co-working spaces, a VPN is not just a best practice; it is an essential tool for protecting company assets and personal privacy.
Enterprise-grade solutions from industry leaders like Cisco Systems and Palo Alto Networks have long been the standard for corporate environments. For businesses of all sizes, services like NordLayer offer dedicated business VPNs designed for team management and secure remote access. These tools prove that securing remote connections is achievable and scalable for any organization.
How to Implement a VPN
Setting up a VPN for your remote team involves more than just installing software. A strategic approach ensures both security and performance are optimized for your workforce.
- Choose the Right Provider: Select a business-focused VPN provider with a strict no-logs policy to ensure user activity is not stored. Evaluate features like centralized billing, dedicated IP addresses, and user management capabilities.
- Configure for Your Needs: Implement an “always-on” VPN configuration for employees handling highly sensitive data, forcing all traffic through the secure tunnel. For others, consider using split tunneling, which routes only company-related traffic through the VPN to conserve bandwidth and improve performance.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly push updates for the VPN client software to all employee devices. These updates often contain critical security patches that protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Educate Your Team: Train employees on when and how to use the VPN correctly. Emphasize the importance of activating it whenever they are connected to a network outside the office to maintain a consistent security posture.
4. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Traditional antivirus software relies on known malware signatures, making it ineffective against new, sophisticated threats. In a remote work environment where employee devices connect from countless networks, this reactive approach is insufficient. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) offers a modern, proactive solution, functioning like a 24/7 security guard for every endpoint.
EDR is a cybersecurity technology that continuously monitors end-user devices like laptops, desktops, and mobile phones to identify and respond to cyber threats in real time. It goes beyond simple malware scanning by recording system activities and events, analyzing this data for suspicious patterns, and providing tools to investigate and remediate security incidents. If a threat is detected, EDR can automatically isolate the affected device to prevent the threat from spreading across the network.
Why EDR is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
EDR is essential for securing a distributed workforce because it provides deep visibility into the very devices that are your organization’s new perimeter. It addresses the reality that remote endpoints are prime targets for attackers. By continuously monitoring for indicators of compromise, EDR helps security teams detect stealthy attacks that would otherwise go unnoticed, such as fileless malware or advanced persistent threats. This makes it one of the most critical remote work security best practices for any modern organization.
Leading cybersecurity firms have demonstrated EDR’s power. CrowdStrike’s Falcon platform and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint are prominent examples that provide comprehensive visibility and automated response capabilities. These platforms enable security teams to hunt for threats proactively and respond to incidents swiftly, no matter where the endpoint is located.
How to Implement EDR
Deploying an EDR solution requires more than just installing software. A strategic approach ensures you get the maximum benefit from this powerful technology. To implement EDR effectively, consider these actionable steps:
- Establish Clear Incident Response Procedures: Define who is responsible for what when an alert is triggered. A clear, documented plan ensures a fast and coordinated response, minimizing potential damage.
- Tune Detection Rules: Out of the box, EDR solutions can generate many false positives. Work with your team to customize and tune detection rules based on your organization’s specific environment and typical user behavior to reduce alert fatigue.
- Integrate with a SIEM: For a holistic security view, integrate your EDR solution with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system. This allows you to correlate endpoint data with logs from other sources, like firewalls and servers, for more accurate threat detection.
- Provide Regular Training: Ensure your security team is proficient in using the EDR platform. Regular training and drills on threat hunting and incident response will keep their skills sharp and your organization prepared.
5. Secure Cloud Storage and Data Loss Prevention
As remote work shifts data from on-premise servers to cloud-based platforms, the risk of data leaks, unauthorized access, and compliance violations escalates. A strategy for Secure Cloud Storage and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) addresses this by creating a protective shield around your digital assets, no matter where they are stored or accessed. It combines strong encryption, granular access controls, and intelligent monitoring to safeguard sensitive information.
This approach goes beyond basic cloud security by actively preventing data exfiltration. DLP tools scan outbound data streams for sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or intellectual property, and can block or flag transmissions that violate predefined security policies. This ensures that sensitive data doesn’t accidentally or maliciously leave your controlled environment via email, file sharing, or other channels.
Why Secure Cloud Storage and DLP are Top Remote Work Security Best Practices
For a distributed team, secure cloud storage is the digital equivalent of a secure office file cabinet, but with far more sophisticated locks. Implementing a robust DLP strategy is one of the most critical remote work security best practices because it provides an automated safety net against human error, which is a leading cause of data breaches. It helps enforce data handling policies consistently across a workforce that may be spread across different continents and regulatory environments.
Leading enterprise solutions like Microsoft Information Protection for Office 365 and Google Cloud’s Data Loss Prevention API demonstrate how these systems can be integrated seamlessly into daily workflows. These tools automatically classify and label data, apply encryption, and monitor sharing activities, making security an invisible but powerful part of the user experience.
How to Implement Secure Cloud Storage and DLP
Deploying a comprehensive data protection strategy requires careful planning. To effectively secure your cloud environment and prevent data loss, follow these actionable steps:
- Start with Data Discovery: You can’t protect what you don’t know you have. Use data discovery tools to identify where your sensitive data resides across all cloud storage platforms, then classify it based on its level of sensitivity.
- Implement Policies Gradually: Begin with a “monitor-only” mode to understand how data is currently being shared. Use this insight to build and refine your prevention policies, rolling them out to small user groups first to gather feedback and minimize disruption.
- Automate Encryption: Configure your cloud storage to automatically encrypt sensitive files both at rest (stored on the server) and in transit (as they are being uploaded or downloaded). This ensures data is unreadable even if intercepted.
- Audit Access Permissions Regularly: Periodically review and audit who has access to what data. Enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring employees only have access to the information absolutely necessary for their roles. If you want to dive deeper, you can learn more about data privacy best practices for remote work to enhance your security posture.
6. Regular Security Awareness Training
The most advanced security technology can be rendered useless by a single human error. In a remote work setting, where employees are the first line of defense, a well-informed team is your greatest security asset. Regular Security Awareness Training shifts the focus from purely technological defenses to building a security-conscious culture, empowering employees to recognize and respond to threats.
This practice involves ongoing educational programs that keep your distributed team updated on the latest cybersecurity threats, from sophisticated phishing schemes to social engineering tactics. Instead of a one-time onboarding session, it’s a continuous process that reinforces secure habits and adapts to the evolving threat landscape. The core principle is simple: a trained human firewall is often the most effective.


Why Regular Training is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
Remote employees operate outside the traditional office’s physical security and IT support bubble, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. Regular training directly mitigates this risk by equipping them with the knowledge to identify suspicious emails, secure their home networks, and handle sensitive data appropriately, no matter where they are. This proactive approach turns potential liabilities into vigilant defenders of company assets.
Pioneering platforms like KnowBe4 and Proofpoint have demonstrated that continuous, engaging training significantly reduces successful phishing attacks and other security incidents. By using real-world simulations and interactive content, they transform abstract security policies into practical, memorable skills, making this one of the most impactful remote work security best practices for strengthening your human element.
How to Implement Security Awareness Training
Effective training is more than just sending out an annual memo. To build a robust program that resonates with remote workers, focus on continuous engagement and practical application.
- Make it Engaging and Frequent: Replace long, annual training sessions with short, monthly or quarterly modules. Use gamification, interactive quizzes, and real-world scenarios to maintain interest and improve retention.
- Run Phishing Simulations: Regularly test employees with simulated phishing emails. Provide immediate, non-punitive feedback to those who click, explaining the red flags they missed. This hands-on experience is incredibly effective.
- Tailor Content to Roles: Customize training materials based on an employee’s role and access to sensitive data. A developer needs different security insights than a marketing specialist.
- Create a Security Resource Hub: Establish a centralized, easily accessible place for all security policies, training materials, and contact information for the security team. This empowers employees to find answers quickly when they have a question or concern.
7. Device Management and Mobile Device Management (MDM)
When employees use personal laptops, tablets, and smartphones for work, your company’s attack surface expands exponentially. Device Management and Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms provide a centralized way for IT administrators to secure, monitor, and enforce policies on any endpoint accessing corporate data, regardless of who owns it. This technology is a cornerstone of modern remote work security best practices.
MDM solutions allow businesses to enforce security standards such as mandatory passcodes, data encryption, and the installation of approved applications. If a device is lost or stolen, an administrator can remotely wipe corporate data to prevent a breach. This ensures a consistent security baseline across a diverse fleet of devices, from company-issued laptops to employee-owned smartphones (BYOD).
Why MDM is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
Implementing MDM is essential for any organization with a remote or hybrid workforce. It closes the significant security gaps created by unmanaged devices accessing sensitive information from various locations. Without MDM, a single compromised personal device could provide an attacker with an unguarded entry point into your entire corporate network. It provides control and visibility where it’s needed most: at the endpoint.
Pioneers in this space, such as AirWatch (now VMware Workspace ONE) and MobileIron (now part of Ivanti), established the importance of managing mobile endpoints. Today, comprehensive solutions like Microsoft Intune and Jamf (for Apple devices) offer robust platforms that integrate seamlessly into existing IT ecosystems, making enterprise-grade security accessible for businesses of all sizes.
How to Implement Device Management and MDM
Rolling out a device management solution requires a clear strategy that balances security with user privacy and productivity. To implement MDM effectively, follow these actionable steps:
- Establish a Clear BYOD Policy: Create a formal Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy that outlines user responsibilities, what data can be accessed, and the security measures that will be enforced. Transparency is key to user adoption.
- Use Containerization: Separate work and personal data on employee devices using containers. This protects corporate information without infringing on the user’s personal privacy, a common concern that can hinder MDM adoption.
- Implement Graduated Responses: Define automated actions for non-compliant devices. For example, a device that misses a security patch might temporarily lose access to email, while a jailbroken phone could be blocked from the network entirely.
- Audit Devices Regularly: Schedule regular audits of all managed devices to ensure they remain compliant with your security policies and to remove any stale or unauthorized endpoints from your system. These are crucial safety tips for remote workers at home, and you can learn more about securing your personal devices on remotetribe.life.
8. Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Just as ships have watertight compartments to contain flooding, secure networks use segmentation to contain breaches. Network segmentation involves dividing a larger network into smaller, isolated sub-networks or segments. This structure controls the flow of traffic between them, ensuring that a security incident in one area doesn’t spread across the entire organization.
Micro-segmentation takes this concept to an even more granular level. Instead of just segmenting parts of the network, it creates secure zones around individual workloads or applications. This approach effectively wraps each critical asset in its own security perimeter, drastically limiting an attacker’s ability to move laterally once inside the network. It’s a key component of a robust Zero Trust strategy.
Why Segmentation is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
In a remote work environment, employees connect from countless locations, effectively dissolving the traditional network perimeter. Segmentation addresses this by creating internal checkpoints that protect sensitive data, even if an attacker gains initial access through a compromised remote endpoint. If a remote worker’s laptop is infected with malware, segmentation can prevent that malware from reaching critical servers or databases.
This method contains the “blast radius” of any security incident. Leading platforms like VMware’s NSX and Illumio Core have pioneered micro-segmentation, enabling organizations to apply security policies directly to applications regardless of where they are hosted. This application-centric approach is one of the most effective remote work security best practices for protecting distributed assets from sophisticated threats.
How to Implement Network Segmentation
Implementing segmentation requires careful planning and execution. It is a powerful strategy that can be rolled out incrementally to secure your most valuable resources first.
- Map Your Environment: Before creating segments, you must understand how your applications and data communicate. Use traffic analysis tools to map dependencies and identify critical communication pathways.
- Start with Broad Segments: Begin with macro-segmentation by separating key environments, such as development, testing, and production. This provides immediate value and serves as a foundation for more granular controls.
- Embrace Automation: Manually managing thousands of micro-segmentation policies is not feasible. Leverage automation platforms to create, enforce, and update security policies dynamically as your environment changes.
- Pilot with a Non-Critical Application: Test your segmentation strategy on a low-impact application first. This allows you to refine policies and troubleshoot issues without disrupting core business operations.
9. Incident Response and Business Continuity Planning
Even with the best preventative measures, security incidents can still occur. An Incident Response and Business Continuity Plan (IRP/BCP) provides a structured framework for detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents while ensuring critical business operations continue with minimal disruption. It’s the essential playbook for what to do when things go wrong, especially when your team is geographically dispersed.
This comprehensive plan outlines predefined procedures, communication protocols, and recovery strategies specifically adapted for remote work environments. It assumes a breach will happen and focuses on minimizing its impact, from initial detection to post-incident analysis. A well-defined plan ensures a coordinated, calm, and effective response instead of a chaotic scramble, which is a critical advantage when team members are not in the same physical location.
Why an IRP/BCP is a Top Remote Work Security Best Practice
A robust IRP/BCP is a non-negotiable component of modern remote work security best practices. The distributed nature of remote work complicates incident response; you can’t simply walk over to an employee’s desk to isolate a compromised machine. This plan provides the necessary structure, clearly defining roles, communication channels, and technical procedures to manage an incident across different time zones and locations. It turns a potential catastrophe into a manageable event.
Leading cybersecurity firms like FireEye Mandiant and IBM X-Force have built their reputations on helping organizations develop and execute these plans, proving their value in real-world crises. These frameworks, along with guidance from institutions like NIST and the SANS Institute, establish a gold standard for preparing for and handling security breaches in any environment, including a fully remote one.
How to Implement Incident Response and Business Continuity Planning
Developing a plan that works for a remote team requires careful thought and preparation. To create an effective IRP/BCP, follow these actionable steps:
- Develop Specific Playbooks: Create step-by-step guides for common incident types like ransomware attacks, phishing-led account takeovers, and data breaches. Tailor these playbooks for a remote context, including instructions for remotely isolating devices.
- Establish Clear Roles: Designate an incident response team with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Ensure everyone knows who to contact and who has the authority to make critical decisions, regardless of their physical location.
- Practice with Tabletop Exercises: Regularly conduct simulated incident drills. These tabletop exercises help your remote team practice the plan, identify gaps, and build the muscle memory needed to act decisively during a real event.
- Maintain Updated Communication Channels: Keep contact lists and emergency communication channels (e.g., a dedicated Slack channel or a secure messaging app) current and easily accessible to all team members.
For a deeper dive into creating a resilient strategy, you can explore detailed guides on Incident Response and Business Continuity Planning.
Remote Work Security Best Practices Overview
| Security Solution | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Trust Network Architecture | High – complex phased deployment | High – requires continuous monitoring | Strong threat reduction and granular control | Remote work, highly regulated environments | Reduces attack surface, limits lateral movement |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Low to Medium – relatively easy | Low – mostly software/hardware tokens | Significant reduction in account takeovers | User authentication for apps/accounts | Blocks 99.9% automated attacks, cost-effective |
| Virtual Private Network (VPN) Implementation | Medium – setup and maintenance needed | Medium – requires server/client software | Secure remote access with encrypted tunnels | Remote access to internal networks | Encrypts all traffic, location privacy |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | High – requires skilled analysts | High – resource intensive on endpoints | Rapid threat detection and automated response | Endpoint security in enterprises | Comprehensive visibility, faster detection |
| Secure Cloud Storage & Data Loss Prevention | Medium – policy and tech integration | Medium to High – encryption and monitoring | Data protection, regulatory compliance | Cloud data protection, compliance-focused | Data breach risk reduction, audit trails |
| Security Awareness Training | Low to Medium – continuous program | Low – time and training resource investment | Reduced human error, improved security culture | All organizations, especially remote teams | Cost-effective, improves incident reporting |
| Device & Mobile Device Management (MDM) | Medium to High – device/admin setup | Medium – ongoing management | Enforces security policies on devices | BYOD and remote workforce device control | Centralized management, remote wipe |
| Network Segmentation & Micro-segmentation | High – requires network redesign | High – requires ongoing policy management | Limits threat spread, improves network safety | High-security networks, sensitive data zones | Reduces breach impact, detailed visibility |
| Incident Response & Business Continuity | High – planning and documentation | High – skilled personnel and testing | Minimized downtime, faster recovery | Incident handling, regulatory compliance | Builds resilience, clear procedures |
Building Your Digital Fortress, One Practice at a Time
The transition to a remote-first world offers unparalleled freedom and flexibility, but this new frontier is not without its perils. As we’ve explored, navigating the digital landscape as a remote professional requires more than just a reliable internet connection; it demands a proactive and deeply ingrained security mindset. The nine remote work security best practices detailed in this guide are not just isolated recommendations but interconnected pillars that form a comprehensive defensive strategy. They represent a shift from a traditional, perimeter-based security model to a modern, identity-centric approach fit for the work-from-anywhere era.
Adopting these practices means fundamentally changing how you view your digital workspace. It’s about moving beyond the simple “set it and forget it” mentality of installing an antivirus program. Instead, you are constructing a resilient, multi-layered digital fortress where every access point is verified, every device is managed, and every byte of data is protected. This is the essence of a robust security posture in 2024 and beyond.
From Theory to Action: Your Security Roadmap
The journey to becoming a security-savvy remote professional can feel daunting, but it begins with small, consistent actions. The key is to transform these best practices from a checklist into a set of ingrained habits.
- Start with the Foundation: If you do nothing else, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on every single account that offers it. This single action is one of the most effective ways to prevent unauthorized access, acting as a powerful deterrent against credential theft.
- Secure Your Connection: Never connect to public Wi-Fi without activating a reputable Virtual Private Network (VPN). This simple habit encrypts your traffic, effectively cloaking your online activities from prying eyes on unsecured networks in cafes, airports, and coworking spaces.
- Adopt a “Never Trust, Always Verify” Mindset: Embrace the core principle of Zero Trust Architecture. Get into the habit of questioning every access request, even if it appears to come from a known source. This vigilance is your first line of defense against sophisticated phishing and social engineering attacks.
Implementing more advanced strategies like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or Network Segmentation may require more technical expertise or investment, but they build upon these foundational habits. Each practice you adopt adds another layer of steel to your digital fortress, making it progressively harder for threats to penetrate.
The True Value of Proactive Security
Mastering these remote work security best practices is not merely about avoiding a data breach or financial loss, although those are critical outcomes. The true value lies in the confidence and peace of mind it provides. When you know your digital life is secure, you unlock the ability to focus completely on your work, creativity, and the unique experiences that the remote lifestyle affords. You are no longer burdened by the persistent, low-level anxiety of “what if.”
This proactive stance on security transforms you from a potential victim into a formidable target. It demonstrates professionalism to clients and employers, showing that you take the protection of their sensitive information as seriously as your own. In a competitive remote job market, being a security-conscious professional is a powerful differentiator. It’s about building a reputation for reliability and trustworthiness, one secure connection at a time. The ultimate goal is to make security so integral to your workflow that it becomes second nature, allowing you to thrive and innovate without fear in your work-from-anywhere career.
Ready to elevate your security knowledge and connect with a community that prioritizes safe and successful remote work? Remote Tribe is your dedicated resource for expert-led courses, in-depth guides, and a network of like-minded professionals all focused on mastering the digital nomad lifestyle securely.
Join us at Remote Tribe to access the tools and support you need to build your digital fortress with confidence.